What is the importance of TBW in SSD hard?
After years of using your old HDD or even consuming your SSD heavily, now is the time to buy a new SSD storage. In the event that you have already made the decision and started the search for the best SSD for your computer, you have probably seen a lot of comparisons on the Internet. Among the various standards used for comparison, the TBW value is often repeated as an important criterion when choosing or evaluating an SSD and you don't know what it means exactly. Now, if I told you that the TBW value represents the endurance of the SSD storage, would you know what that means and why it matters? In this topic, we will explain the meaning of TBW and what it means exactly, so follow the next lines with us.
SSD storage endurance measure
Of course, the word TBW is an acronym, where the full designation is TeraBytes Written, and it is a measure that expresses the total number of data that can be written "cumulatively" on the SSD storage unit over the period of its use. This number is, of course, measured in terabytes, which is equivalent to a thousand gigabytes. It, in other words, refers to the amount of data written to the SSD before it fails. Let's apply an example for clarification. If the SSD hard drive is designed to hold 400 TBW, this means that the user can write a total of 400 TB of data on the hard drive before he needs to purchase another storage unit. Simple and uncomplicated, this number gives an impression of the SSD storage capacity.
It is worth noting that the term TBW is sometimes expressed as an acronym for another designation, which is Total Bytes Written, or the sum of written data so that the amount of data is not required to be expressed in terabytes, but rather more than that, as many enterprise SSDs are used TBW or Total Bytes Written is a measurement of data size expressed in petabytes or one million terabytes.
What is the significance of the TBW value?
Because they operate differently from conventional hard disks (HDD), SSD storage systems have a shorter lifespan as a result. The role of the TBW scale here is very important since it definitively indicates the life cycle of the hard drive in general. Within NAND flash memories, the SSD units store data in the form of cells. These cells are not affected by reading the data, but rather deteriorate every time the current data is deleted and new data is written, they end up having flash memory that is unable to store new information. This frequently occurs over time and has a significant impact on the SSD's overall performance. This is why the TBW value is important for determining how much data you can write before the SSD storage becomes unusable.
The TBW scale is directly proportional to the larger SSD units because they have a greater number of NAND Flash memory cells dedicated to storing data. For example, a 256GB SSD has a value of 150TBW, while a 512GB SSD has a value of 300TBW. Also, the SSD units intended for organizations and servers have a larger scale than those intended for ordinary users or home use, as well as for luxury disks intended for a specific class of customers.
Although the TBW metric is relied upon as an accurate measure of the lifespan of SSDs, it is impossible for the overwhelming majority of ordinary users to reach the full consumption of the specified TBW value during the life cycle of their hard drives. So if you're not using your SSD to write or store hundreds of gigabytes of data every day, you don't have to worry about that scale!
The truth is that the TBW value is only important when using the SSD as an internal or main storage unit to host the operating system on the computer, in which case data is frequently written to the NAND memory unlike using the SSD as an external hard drive, and here the user will often write Data on it intermittently either to store important files or to backup files from time to time. In any case, it is important to know that the higher the value of the TBW, the better it is, but it will be reflected in the price of the SSD, as it represents an “advantage”. So it's better to balance your needs, so don't waste your money on a TBW-value SSD that won't reach you until after decades of depreciation, and at the same time don't waste your money on buying an SSD that will only last a few months!
What about the DWPD value too?
TBW isn't the only metric that expresses the age of an SSD. Another term is called DWPD, which is an acronym for Drive Writes Per Day. As is clear from the name, it expresses the shelf life of a storage unit by a certain amount of data that is written across the entire storage memory every day, during a specific period usually the warranty period. For example, if the DWPD value of the SSD is 5 and the warranty period is two years, this means that the hard drive will bear writing 5 terabytes of data per day for two full years. 10 terabytes of data per day over the course of an entire year, and so forth.
The DWPD metric is most commonly used for enterprise SSDs, while the TBW metric is most commonly used for consumer SSDs. In the event that the manufacturer did not mention the value of the DWPD, you can find it using the value of TBW through a simple calculation that can be formulated as follows: DWPD scale = TBW scale ÷ (number of warranty years x 365 x SSD storage capacity).
How to find out the TBW value
Whether you own an SSD or intend to purchase a new storage unit for your device, it is important to know the TBW value in order to have an idea of the unit's lifespan. And let me tell you that the matter is very simple, as all you have to do is view the web page of the SSD model on the official website of the manufacturer, or you will find the value written in the list of specifications printed on the packaging box. It is worth noting that the TBW value usually ranges from 30 TB to a few thousand, depending on each model and storage capacity. As we mentioned, a higher TBW value indicates greater endurance, while a decrease indicates poorer endurance.
How do I know the amount of data written on my SSD?
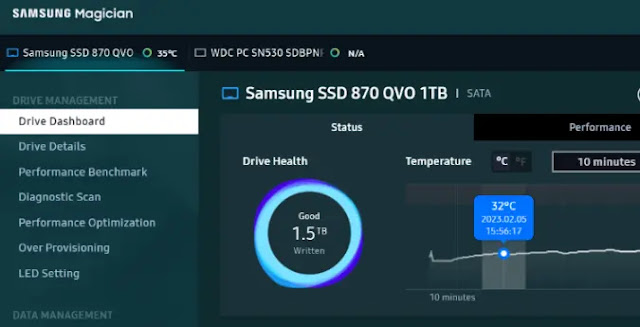
After knowing the standard TBW value for your SSD, you may want to check whether the hard has reached this value or the amount of data written so far. For this purpose, you can simply compare the benchmark value with the total amount of data written to the SSD since the day it was used. This process is facilitated by CrystalDiskInfo for Windows or DriveDX for Mac or even SSD management software developed by manufacturers such as Samsung Magician.
Through the official program from the company, you can know the total written data, along with many other information and details that are collected by the S.M.A.R.T technology integrated into the storage unit. However, you will search the program for the term Data Units Written, Total Host Writes, or TB Written. Usage may be measured in terabytes or gigabytes. In the latter case, you must convert the value to terabytes by dividing by 1,024 and then comparing it to the TBW value. If the memory consumption is 100 terabytes and the TBW value, for example, is 200, then this means that only half may remain.
What happens when the TBW value is exceeded?
Let's say that you have accomplished what we previously deemed to be impossible, namely draining or even exceeding the TBW amount. This does not mean that the SSD unit is no longer of much use, or rather it has become dead! The memory will be able to read the data that is currently stored there, but writing new data will be challenging. Because manufacturers set the standard TBW value conservatively, SSDs typically continue to function even after it has been exceeded.
In general, S.M.A.R.T. technology will automatically disable the ability to store new data and set the volume to read-only mode when it detects that there is no longer room to write new data from the SSD storage memories or a warning that it will soon fail. In this state, it will not be able to add any new files, but you will be able to access and move the currently stored files across any other memory of any type.




Post a Comment